7.7: Reading- Folds
- Page ID
- 11484
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Ductile rocks behave plastically and become folded in response to stress. Even in the shallow crust where rocks are cool and relatively brittle, folding can occur if the stress is slow and steady and gives the rock enough time to gradually bend. If the stress is applied too quickly, rocks in the shallow crust will behave as brittle solids and break. Deeper in the crust, where the rocks are more ductile, folding happens more readily, even when the stress and strain occurs rapidly.
Anticlines and Synclines
The most basic types of folds are anticlines and synclines. Imagine a rug, the sides of which have been pushed toward each other forming ridges and valleys – the ridges are “up” folds and the valleys are “down” folds. In terms of geologic structures, the up folds are called anticlines and the down folds are called synclines.
In block diagrams like those shown below, the top of the block is the horizontal surface of the earth, the map view. The other two visible sides of the box are cross-sections, vertical slices through the crust. The colored layers represent stratified geologic formations that were originally horizontal, such as sedimentary beds or lava flows. Use the block diagrams to visualize the three-dimensional shapes of the geologic structures. Keep in mind that erosion has stripped away the upper parts of these structures so that map view reveals the interior of these structures.

In map view, an anticline appears as parallel beds of the same rock type that dip away from the center of the fold. In an anticline, the oldest beds, the ones that were originally underneath the other beds, are at the center, along the axis of the fold. The axis is an imaginary line that marks the center of the fold on the map.
In map view, a syncline appears as a set of parallel beds that dip toward the center. In a syncline the youngest beds, the ones that were originally on top of the rest of the beds, are at the center, along the axis of the fold.
Anticlines and synclines form in sections of the crust that are undergoing compression, places where the crust is being pushed together.
Plunging Anticlines and Synclines
A plunging anticline or a plunging syncline is one that has its axis tilted from the horizontal so that the fold is plunging into the earth along its length. Plunge direction is the direction in which the axis of the fold tilts down into the earth.
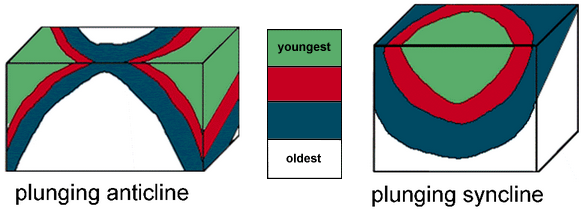
In map view, a plunging anticline makes a U-shaped or V-shaped pattern that points, or closes, in the direction of plunge. A cross-section at a right angle to the axis of a plunging anticline looks the same as an anticline.
In map view, a plunging syncline makes a U-shaped or V-shaped pattern that opens in the direction of plunge.
Anticlines

In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up. Therefore if age relationships between various strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used.
On a geologic map, anticlines are usually recognized by a sequence of rock layers that are progressively older toward the center of the fold because the uplifted core of the fold is preferentially eroded to a deeper stratigraphic level relative to the topographically lower flanks. The strata dip away from the center, or crest, of the fold.

If an anticline plunges (i.e., is inclined to the Earth’s surface), the surface strata will form Vs that point in the direction of plunge. Anticlines are often flanked by synclines although faulting can complicate and obscure the relationship between the two. Folds often form during crustal deformation as the result of shortening that accompanies orogenic mountain building. In many cases anticlines are formed by movement on non-planar faults during both shortening and extension, such as ramp anticlines and rollover anticlines.
Terminology
Any fold whose form is convex upward is an antiform. Antiforms containing progressively younger rocks from their core outwards are anticlines.
An anticline or antiform has a crest, which is the highest point on a given stratum along the top of the fold. A hinge in an anticline is the locus of maximum curvature or bending in a given stratum in the fold. An axis is an imaginary line connecting the hinges in the different strata in a two-dimensional cross-section through the anticline. Connecting the hinges or points of maximum curvature in the different layers in three dimensions produces an axial plane or axial surface. In a symmetrical anticline, a surface trace of the axial plane coincides with the crest. With an asymmetrical anticline, the surface trace of the axial plane or axis will be offset from the crest toward the steeper flank of the fold. Anoverturned anticline is an asymmetrical anticline with a flank or limb that has been tilted beyond perpendicular so that the beds in that limb are upside-down.
A structure that plunges in all directions to form a circular or elongate structure is a dome. Domes are generally formed from one main deformation event, or via diapirism from underlying magmatic intrusions or movement of upwardly mobile, mechanically ductile material such as rock salt (salt dome) and shale (shale diapir). The Richat Structure of the Sahara is considered a dome that has been laid bare by erosion.
An anticline which plunges at both ends is termed a doubly plunging anticline, and may be formed from multiple deformations, or superposition of two sets of folds, or be related to the geometry of the underlying detachment fault and the varying amount of displacement along the surface of that detachment fault. The highest point on a doubly plunging anticline (or any geologic structure for that matter) is called the “culmination.”
An elongate dome which developed as the sediments were being deposited is referred to as a pericline.
An anticlinorium is a series of anticlinal folds on a regional-scale anticline. Examples include the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous Purcell Anticlinorium in British Columbia and the Blue Ridge anticlinorium of northern Virginia and Maryland in the Appalachians, or the Nittany Valley in central Pennsylvania.
Economic significance

Doubly plunging or faulted anticlines, culminations, and structural domes are favored locations for oil and natural gas drilling; the low density of petroleum causes it to buoyantly migrate upward to the highest parts of the fold, until stopped by a low-permeability barrier such as an impermeable stratum or fault zone. Examples of low-permeability seals that contain the hydrocarbons, oil and gas, in the ground include shale, limestone, sandstone, and even salt domes. The actual type of stratum does not matter as long as it has low permeability.
Periclines are important focal points for pooling of hot, metal-laden formational brines, which can form manto ore deposits, Irish-type lead-zinc deposits and uranium deposits, amongst others.
Culminations in folded strata which are cut by shears and faults are favoured loci for deposition of saddle-reef style lode gold deposits.
Synclines

In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold, termed a synformal syncline (i.e. a trough); but synclines that point upwards, or perched, can be found when strata have been overturned and folded (an antiformal syncline).
Characteristics
On a geologic map, synclines are recognized by a sequence of rock layers that grow progressively younger, followed by the youngest layer at the fold’s center or hinge, and by a reverse sequence of the same rock layers on the opposite side of the hinge. If the fold pattern is circular or elongate circular the structure is a basin. Folds typically form during crustal deformation as the result of compression that accompanies orogenic mountain building.
Notable Examples
- Powder River Basin, Wyoming, USA.
- Sideling Hill roadcut along Interstate 68 in western Maryland, USA, where the Rockwell Formation and overlying Purslane Sandstone are exposed.
- Western Lake Superior, which occupies a basin created by the Midcontinent Rift System
- Saou, a commune in the Drôme department in southeastern France
- The Catlins, an area in the southeastern corner of the South Island of New Zealand
Basins and Domes
A basin is a bowl-like depression in the strata (layers of rock). A basin is similar to a syncline, but instead of an axis it has a single point at the center. The strata all dip toward the center point and the youngest rock is at the center. In map view, the strata form concentric circles – a bull’s eye pattern – around the center point.
A dome is an bulge in strata. A dome is similar to an anticline, but instead of an axis it has a single point at the center. The strata all dip away from the center point and the oldest rock is at the center. In map view, the strata form concentric circles – a bull’s eye pattern – around the center point.
Contributors and Attributions
- Basics -- Geologic Structures. Authored by: Ralph L. Dawes and Cheryl D. Dawes. Provided by: Wenatchee Valley College. Located at: http://commons.wvc.edu/rdawes/G101OCL/Basics/structures.html. Project: Geology 101 - Introduction to Physical Geology. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Anticline. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Anticline. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Syncline. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Syncline. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Sideling Hill cut. Authored by: Acroterion. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Sideling_Hill_cut_MD1.jpg. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike


