5.1: Soil Colloids
- Page ID
- 14727
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
- Measure the effects of different cations on colloidal properties.
- Identify the soil components controlling ion exchange.
- Determine the cation exchange capacity of selected soil horizons.
Colloids consist of clay minerals and organic matter, and play critical roles in soil chemical, physical, and biological properties. Colloids are very small in size. The majority of charges in soil comes from colloids, making them important for cation exchange capacity, buffering capacity, and retention of nutrients like Ca2+, K+, Mg2+, etc. In addition, the small size of colloids leads to very high surface areas, which facilitates chemical reactions and provides habitat for microbes. Some clays expand and contract with changes in soil wetness. The force from expanded clays can be considerable, and commonly cause structural failures in house foundations and basement walls, roads and bridges, and other man-made structures. Other clays do not expand, and make ideal substances for clay pottery, or tile roofs. The organic matter fraction of colloids are important for the development of soil structure, or as food sources for soil organisms. The soil properties attributed to colloids are numerous, and will be the focus of the following laboratory activities.
Materials
- Petri dishes
- Beakers
- Spatulas
- Pure kaolinite
- Pure bentonite
- Caliper
- 6V battery
- Solid copper wires, 2 total, 25 cm long
- Alligator clips for the wires
- Paper towels
- Test tubes
- Flasks
- Burettes
- Bottle-top dispensers set to dispense 10 mL
- Phenolphthalein indicator solution
- Aluminum chloride solution, 1 M
- Potassium chloride solution, 1 M
- Sodium chloride solution, 1 M
- Calcium chloride solution, 1 M
- Sodium hydroxide solution, 0.01 M
- Simulated soil CEC extract solutions
- Norfolk E horizon, 0.002 M HCl
- 10 mL of extract represents 1 g of soil
- Norfolk Bt horizon, 0.005 M HCl
- 10 mL of extract represents 1 g of soil
- Cecil Ap horizon, 0.010 M HCl
- 10 mL of extract represents 1 g of soil
- Cecil Bt Horizon, 0.007 M HCl
- 10 mL of extract represents 1 g of soil
- Whitestore Bt horizon, 0.015 M HCl
- 10 mL of extract represents 0.5 g of soil
Recommended Reading
- Introduction to the Sorption of Chemical Constituents in Soils (Thompson and Goyne, 2012)
- Cation Exchange Capacity and Base Saturation (Sonon et al., 2017)
Prelab Assignment
Using the recommended readings and the introduction to this lab, consider the questions listed below. These definitions/questions will provide a concise summary of the major concepts to be addressed in the lab. They will also serve as the basis for the post-lab quiz and are useful study notes for exams.
- Define the term “soil colloid”. What are the main types of soil colloids?
- Describe the sources of charges on soil colloids.
- Define cation exchange capacity.
- What units are used to express cation exchange capacity?
- List the general quantity of cation exchange capacity contributed by kaolinite, montmorillonite (smectite), and humus.
- Define percent base saturation. What cations are usually considered base cations? Technically speaking they are not bases. Why are they called base cations?
Introduction
The extremely small, colloidal particles (smaller than 0.001 mm) of clay and humus control many important chemical and physical properties of the soil. This portion of the soil is often called the “active fraction”. The small size of colloids results in a large surface area per unit weight, and their ionic structure results in a net electrical charge. The type, amount, and mineralogy of colloids will strongly influence most land management decisions. For example a soil that is 40% of clay that primarily consists of smectite (a 2:1 shrink-swell clay) could have limitations for constructing roads, or building foundations due to the shifting of the soil as the soil wets and dries. Such a soil could be highly productive for row crop agriculture though, due to the high amount of charge that facilitates the retention of nutrients like Ca2+, K+, Mg2+, etc. On the contrary, a soil, such as an Oxisol that has 80% clay has colloids that are primarily aluminum and iron oxides, which do not shrink or swell, and have a low amount of charge. Thus, the soil would be well suited for building foundations. However, the high phosphorus fixation capacity, and the limited ability to retain base cations limit the productivity of the soil for row crop agriculture.
Ion exchange is one of the most significant features of the clay and humus fractions. The capacity of the particles to attract or adsorb cations is called the cation exchange capacity. This ability allows the soil to serve as a storehouse of plant nutrients like potassium, calcium, and magnesium. This reactive exchange capacity also permits the soil to serve as a filter or treatment medium for land application of waste materials.
Determining Cation Exchange Capacity
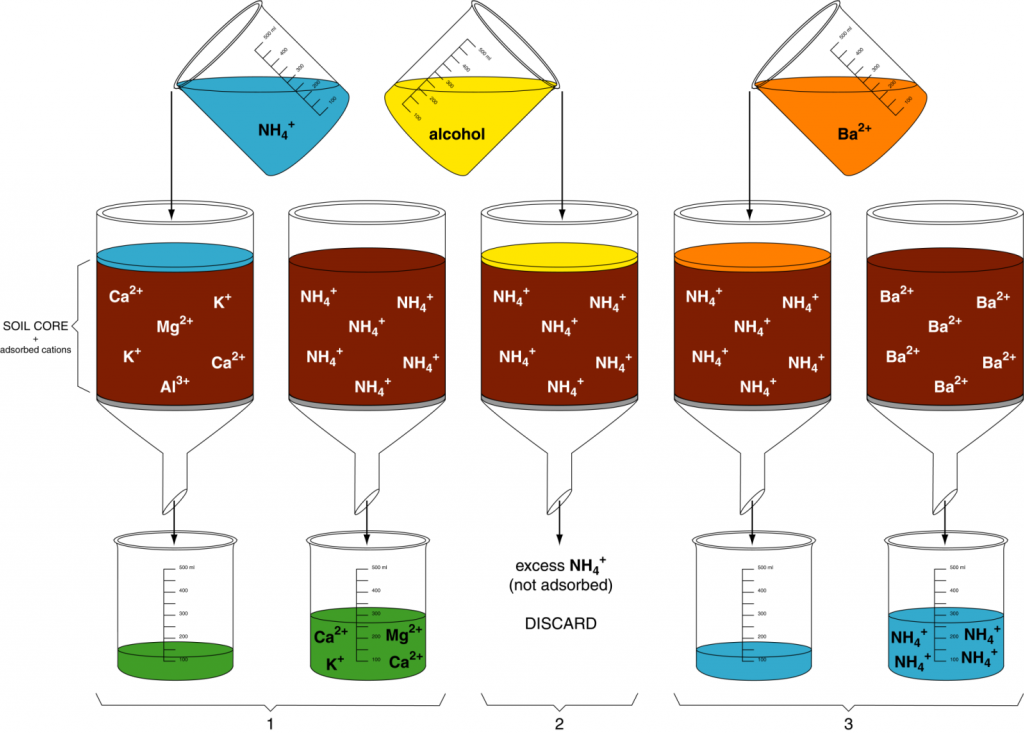
The cation exchange capacity (quantity of cations a soil can adsorb per unit weight, CEC) can be determined using a simple displacement process (Figure 13.1). In step 1, a soil sample is first saturated with a simple cation like NH4+ so all the negative charge sites are occupied by NH4+. In step 2, excess NH4+ (i.e., not on exchange sites) is removed by leaching with ethyl alcohol. In step 3, another cation such as Ba2+ is used to displace all the NH4+. The NH4+ is collected in the filtrate and measured. The quantity of NH4+ collected from the sample is the quantity of cations that the soil can hold, i.e. CEC.
Many cations could be used in step 1 of the displacement method. Soil laboratories often use the ammonium ion. However, in this activity, H+ will be used as the saturating cation. Therefore, we will determine the amount of extracted H+ in the filtrate. Then, using that amount, you will calculate the CEC for each soil sample.
Calculating CEC uses the concept of moles of charge. In chemistry, one mole of an element is the quantity of the element with a weight in grams numerically equal to its atomic weight. For example, the atomic weight of K is 39.1, so one mole of K weighs 39.1 g. One mole of any element contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms of the element. Similarly, one mole of charge is 6.02 x 1023 charges. If K exists as a cation in solution (K+), then a solution containing a mole of K would contain 6.02 x 1023 positive charges.
The number of positive charges in the filtrate is thus equal to the number of negative charges on the exchange sites in the soil sample. Therefore, your task is to determine the number of charges in the filtrate. Each H+ ion has one positive charge, so by determining the amount of H+ in the filtrate, you can determine the number of positive charges in the filtrate and by extension, the number of negative charges on the exchange sites in the soil sample.
Activity 1: Demonstration of Shrink-Swell Characteristics
In a previous lab, you filled two petri dishes with slurries of bentonite and kaolinite and set them aside to dry. Retrieve those petri dishes and perform the following steps:
![]() Measure the height and radius of the discs of bentonite and kaolinite, and record the results in Table 13.1.
Measure the height and radius of the discs of bentonite and kaolinite, and record the results in Table 13.1.
![]() Calculate the volume of each disc, and record the results in Table 13.1.
Calculate the volume of each disc, and record the results in Table 13.1.
![]() Calculate and record the percent volume change in each sample relative to the original volume (interior volume of the empty petri dish).
Calculate and record the percent volume change in each sample relative to the original volume (interior volume of the empty petri dish).
Table 13.1. Shrink-Swell Measurements & Volume Changes
| Sample | Radius (cm) | Height (cm) | Volume (cm^3) | % Volume Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empty petri dish | N/A | |||
| Kaolinite | ||||
| Bentonite |
![]() If you were building a house with a basement, would you prefer the dominant clay mineral of the soil on your lot to be kaolinite or bentonite? Explain.
If you were building a house with a basement, would you prefer the dominant clay mineral of the soil on your lot to be kaolinite or bentonite? Explain.
Activity 2. Demonstrations of Colloid Charge
Using the remaining slurry from Activity 1, your instructor will demonstrate colloid charge to the class. In this demonstration, two wires with alligator clips are attached to a 6V battery: one wire to the positive terminal, and the other to the negative terminal. The two wires are then inserted into the slurry and allowed to react for approximately 15 minutes.
![]() Describe what you observe when the wires are removed from the slurry, and explain the phenomenon that causes this.
Describe what you observe when the wires are removed from the slurry, and explain the phenomenon that causes this.
Activity 3: Demonstration of Flocculation and Dispersion
As you now know, most soil clays have a negative charge that is neutralized to varying degrees by the adsorbed cations. Flocculates or aggregates form most rapidly and are most stable when the soil colloid is most completely neutralized by the adsorbed cation. The amount of neutralization is related to ion size, valence, and concentration. Perform the following experiment to test the effect of various ions on the flocculation of a dispersed soil clay.
- Fill 5 test tubes to 1/2 full with the dispersed clay suspension. Test tube 5, containing the original clay suspension, will be reserved to use as a check.
- Add 10 drops of 1M AlCl3 to test tube number 1.
- Add 10 drops of 1 M KCl to test tube 2.
- Add 10 drops of 1M NaCl to test tube 3.
- Add 10 drops of 1M CaCl2 to test tube 4.
- Shake each suspension thoroughly.
- Observe and record the time that flocculation starts in each tube.
- Continue to observe throughout the remainder of the class period and note the relative size and settling rates of the floccules.
![]() Record your observations in Table 13.2.
Record your observations in Table 13.2.
Table 13.2. Effect of cations on flocculation of a clay suspension.
| Added cation | Relative Size & Settling Rates of Floccules |
|---|---|
| K+ | |
| Na+ | |
| Ca2+ | |
| Al3+ | |
| Check |
Activity 4. Determining CEC by replacing adsorbed cations.
In this activity, you will titrate the filtrate with a 0.01 molar solution of NaOH using phenolphthalein as an indicator. Phenolphthalein changes from colorless to faint pink when the quantity of OH– ions added via the NaOH equals the quantity of H+ ions in the solution (that is, when the pH is raised to 7). For this activity, assume the soil samples have been extracted and the filtrates are now available for analysis.
- Place 10 ml of each filtrate into separate 125 ml flasks. This 10 ml quantity is the amount of filtrate from 1.0 gram of soil.
- Add 10 drops of the phenolphthalein indicator.
- Titrate the extract with the NaOH solution to a faint pink endpoint. The titration must be done very carefully to obtain meaningful results. If you put too much NaOH in the flask and get a bright pink color, discard the solution and repeat the process. In the table below, record the milliliters of NaOH solution used to achieve the endpoint.
![]() Calculate the CEC and record your data in Table 13.3.
Calculate the CEC and record your data in Table 13.3.
Here is an example of how to calculate the CEC, assuming 2.5 mL of NaOH was required to achieve an end point. The reaction occurring during titration is
\[\text{NaOH}+\text{H}^{+}\rightarrow\text{Na}^{+}+\text{H}_2\text{O} \nonumber\]
Thus, one mole of NaOH reacts with one mole of H+. Therefore, at the phenolphthalein end point, moles of NaOH added = moles of H+ in solution.
The solution of 0.01 molar NaOH contains 1 cmol charge per liter (1 cmolc/L). Therefore 2.5 mL NaOH contains
\[\text{cmol}_\text{c}\text{ of NaOH}=2.5\text{ mL NaOH}\times\frac{1\text{ L}}{1000\text{ mL}}\times\frac{0.01\text{ mol NaOH}}{1\text{ L}}\times\frac{1\text{ mol}_\text{c}}{1\text{ mol NaOH}}\times \frac{100\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}{1\text{ mol}_\text{c}}= 0.0025\text{ mol}_\text{c}\text{ NaOH} \nonumber\]
Thus, the CEC is
\[\frac{\text{cmol}_\text{c}}{\text{kg soil}}= \frac{0.0025\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}{1\text{ g soil}}\times\frac{1000\text{ g soil}}{1\text{ kg soil}}= \frac{2.5cmolc}{\text{kg soil}} \nonumber\]
Table 13.3. CEC calculations.
| Extract | Molarity of NaOH | Milliliters NaOH used | Wt. of soil | CEC | % Clay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norfolk E | 0.01 | 1 g | 9 | ||
| Norfolk Bt | 0.01 | 1 g | 37 | ||
| Cecil Ap | 0.01 | 1 g | 13 | ||
| Cecil Bt | 0.01 | 1 g | 51 | ||
| White Store Bt | 0.01 | 0.5 g | 57 |
![]() Using the data from Table 13.3, construct a graph in Figure 13.2 with percent clay on the X-axis and CEC on the Y-axis. Label the axes and plot all data. Draw a line through the points on the graph for the Norfolk E, Norfolk Bt, and Cecil Bt, and answer the following questions:
Using the data from Table 13.3, construct a graph in Figure 13.2 with percent clay on the X-axis and CEC on the Y-axis. Label the axes and plot all data. Draw a line through the points on the graph for the Norfolk E, Norfolk Bt, and Cecil Bt, and answer the following questions:
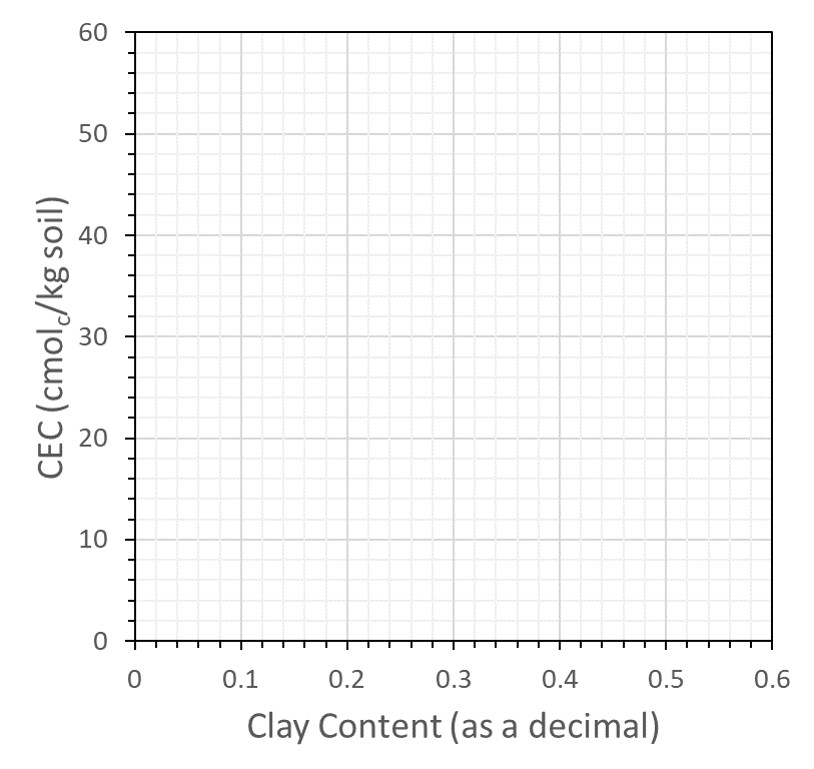
![]() Of the four major factors that affect soil CEC (amount of clay, type of clay, amount of humus, pH), which is responsible for this linear increase in CEC?
Of the four major factors that affect soil CEC (amount of clay, type of clay, amount of humus, pH), which is responsible for this linear increase in CEC?
![]() The slope of the line represents the change in CEC divided by the change in clay content. By expressing clay content as a fraction (for example, 30% clay = 0.30 kg clay/kg soil), the slope becomes
The slope of the line represents the change in CEC divided by the change in clay content. By expressing clay content as a fraction (for example, 30% clay = 0.30 kg clay/kg soil), the slope becomes
\[\text{Slope}=\frac{\Delta\frac{\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}{\text{kg soil}}}{\Delta\frac{\text{kg clay}}{\text{kg soil}}}=\frac{\text{max CEC}-\text{min CEC}}{\text{max clay}-\text{min clay}}=\text{______}\frac{\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}{\text{kg clay}} \nonumber\]
![]() The calculated slope is the CEC on a clay basis. Using that slope (cmolc/kg clay), use Figure 13.2 to determine the type of clay in the Norfolk and Cecil soils.
The calculated slope is the CEC on a clay basis. Using that slope (cmolc/kg clay), use Figure 13.2 to determine the type of clay in the Norfolk and Cecil soils.
![]() The line you have drawn does not pass through the origin, indicating that a soil with no clay would still have CEC. How could this be possible?
The line you have drawn does not pass through the origin, indicating that a soil with no clay would still have CEC. How could this be possible?
![]() The Cecil Ap horizon sample falls just above the line you drew in question #1, yet both Cecil samples were taken from the same profile. How can you explain this difference in CEC?
The Cecil Ap horizon sample falls just above the line you drew in question #1, yet both Cecil samples were taken from the same profile. How can you explain this difference in CEC?
![]() The CEC for the White Store Bt horizon does not fall on the line for the Norfolk and Cecil soil either. Explain what may be different about the colloids in the White Store Bt soil.
The CEC for the White Store Bt horizon does not fall on the line for the Norfolk and Cecil soil either. Explain what may be different about the colloids in the White Store Bt soil.
Example Calculations of Cation Exchange Capacity
Assume a soil has a CEC of 1.0 cmolc/kg. How many kg of Ca2+ can be adsorbed in a hectare of soil to a depth of 20 cm? Assume a bulk density of 1.4 Mg/m3.
Soil volume = area depth:
\[\text{Soil volume}=10,000\text{ m}^2\times0.2\text{ m}=2,000\text{ m}^3 \nonumber\]
Soil weight = density volume:
\[\text{Soil weight}=1.4\frac{\text{Mg}}{\text{m}^3}×2,000\text{ m}^3=2,800\text{ Mg}=2,800,000\text{ kg} \nonumber\]
Because Ca has a valence of 2, one mole of Ca has 2 moles of charge:
\[\frac{2\text{ mol}_\text{c}}{1\text{ mol Ca}|^{2+}} \nonumber\]
The soil can adsorb 1.0 cmolc/kg. The amount of Ca required to supply this amount of charge is
\[\frac{1\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}{\text{kg soil}}\times\frac{1\text{ cmol Ca}^{2+}}{2\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}=\frac{0.5\text{ cmol Ca}^{2+}}{\text{kg soil}} \nonumber\]
The atomic weight of Ca is 40.078, so the soil can adsorb
\[\frac{0.5\text{ cmol Ca}^{2+}}{\text{kg soil}}\times\frac{1\text{ mol Ca}^{2+}}{100\text{ cmol Ca}^{2+}}\times\frac{40.078\text{g Ca}^{2+}}{1\text{mol Ca}^{2+}}=\frac{0.20\text{ g Ca}^{2+}}{\text{kg soil}} \nonumber\]
The quantity of Ca adsorbed in the total soil volume is
\[\frac{0.20\text{ g Ca}^{2+}}{\text{ kg soil}}\times\frac{2,800,000\text{ kg soil}}{1\text{ ha}}\times\frac{1\times\text{ kg Ca}^{2+}}{1000\text{ g Ca}^{2+}}=\frac{560\text{ kg Ca}^{2+}}{ha} \nonumber\]
In the problem above, how much Al3+ could be adsorbed by the soil?
Because the valence of Al is 3, one mole of Al has 3 moles of charge. Thus, the soil, which has 1 cmolc/kg, can adsorb
\[\frac{1\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}{\text{kg soil}}× \frac{1\text{cmol Al}^{3+}}{3\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}=\frac{0.33\text{ cmol Al}^{3+}}{\text{kg soil}} \nonumber\]
The atomic weight of Al is 26.981538 so the soil can adsorb
\[\frac{0.33\text{ cmol Al}^{3+}}{\text{kg soil}}\times\frac{1\text{ mol Al}^{3+}}{100\text{ cmol Al}^{3+}}\times\frac{26.982\text{ g Al}^{3+}}{1\text{ mol Al}^{3+}}=\frac{0.09\text{ g Al}^{3+}}{\text{kg soil}} \nonumber\]
The quantity of Al adsorbed in the total soil volume is
\[\frac{0.09\text{ g Al}^{3+}}{\text{ kg soil}}\times\frac{2,800,000\text{ kg soil}}{1\text{ ha}}\times\frac{1\times\text{ kg Al}^{3+}}{1000\text{ g Al}^{3+}}=\frac{252\text{ kg Al}^{3+}}{ha} \nonumber\]
Cation Exchange Capacity Calculations
Calculate how many kg/ha of the following cations this soil (with a CEC of 1 cmolc/kg) could adsorb.
![]() Mg2+, with an atomic weight of 24.305:
Mg2+, with an atomic weight of 24.305:
![]() Na+, with an atomic weight of 22.990:
Na+, with an atomic weight of 22.990:
![]() H+, with an atomic weight of 1.008:
H+, with an atomic weight of 1.008:
![]() K+, with an atomic weight of 39.098:
K+, with an atomic weight of 39.098:
Base Saturation Calculations
Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, and Na+ are called basic cations because when they are in solution, the solution is basic. In contrast, H+ and Al3+ are considered acidic cations because they lower solution pH.
Therefore, base saturation is
\[\text{Percent base saturation}=\frac{\text{ cmol}_\text{c}\text{ of base cations}}{\text{total CEC of the soil}}\times100\text{%} \nonumber\]
An alkaline soil found in a semi-arid region might have the following cation exchange characteristics (per kg of soil):
- 9.0 cmolc Ca2+
- 2.5 cmolc Mg2+
- 0.5 cmolc K+
- 2.0 cmolc Al3+
- 2.0 cmolc H+
![]() If these cations are the only ones on the exchange sites of this soil, what is the percent base saturation?
If these cations are the only ones on the exchange sites of this soil, what is the percent base saturation?
Activity 5. Calculating versus estimating CEC
There are two ways you can calculate the CEC: the sum of cations method and the mineralogy method.
The Sum-of-Cations Method
If you have a soil analysis where the quantities of all cations in the soil are listed, simply summing all those exchangeable quantities will yield the CEC you found in the preceding problems.
The “Mineralogy” Method
As you know from your reading and class discussion, clay minerals have a range of values for CEC. If the mineralogy of the clay fraction is known (that is, the type and amounts of each clay mineral), then the CEC can be approximated.
To make these calculations easier, Table 13.4 contains representative values for CEC to use in all calculations for this class unless otherwise noted. In nature, however, these soil colloids will have a range of values.
Table 13.4. Typical CEC of various soil colloids.
| Mineral or colloid type | CEC of pure colloid |
|---|---|
| cmolc/kg | |
| kaolinite | 10 |
| illite | 30 |
| montmorillonite/smectite | 100 |
| vermiculite | 150 |
| humus | 200 |
As an example of this mineralogy approach to CEC calculations, consider a soil having 100% clay where the clay is 100% kaolinite. The CEC would then be 10 cmolc/kg. If a soil contains only 10% kaolinite (or 10 kg clay in 100 kg soil), however, this clay would contribute
\[\text{Total CEC of the soil}=\frac{10\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}{\text{kg clay}}\times\frac{10\text{ kg clay}}{100\text{ kg soil}}=\frac{1.0\text{ cmol}_\text{c}}{\text{kg soil}} \nonumber\]
A prairie soil contains 30% clay. This clay sized fraction is dominantly montmorillonite. The soil also contains 5% humus (organic matter).
![]() Using the mineralogy method, what is the cation exchange capacity (CEC) contributed by the clay?
Using the mineralogy method, what is the cation exchange capacity (CEC) contributed by the clay?
![]() What is the estimated cation exchange capacity (CEC) contributed by the humus?
What is the estimated cation exchange capacity (CEC) contributed by the humus?
![]() What is the total estimated CEC of this soil?
What is the total estimated CEC of this soil?
The following is actual laboratory data for the soil in the example:
Table 13.5. Exchangeable cation data
| Exchangeable Acidity | Exchangeable Bases | Exchangeable Bases | Exchangeable Bases | Exchangeable Bases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H+ + Al3+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | K+ | Na+ |
| ----cmolc/kg---- | ----cmolc/kg---- | ----cmolc/kg---- | ----cmolc/kg---- | ----cmolc/kg---- |
| 14.0 | 29 | 10 | 5.5 | 1.5 |
![]() Calculate the CEC from the data in the table using the sum of cations method.
Calculate the CEC from the data in the table using the sum of cations method.
![]() What is the percent base saturation?
What is the percent base saturation?
![]() If you wanted to replace the Na+ with Ca2+, how many kilograms of Ca2+ per 2,800,000 kg of soil would you need?
If you wanted to replace the Na+ with Ca2+, how many kilograms of Ca2+ per 2,800,000 kg of soil would you need?
Assignment: Online Quiz
A quiz for this lab will be available online. Please access it as directed by your instructor.


