13.7: Review and Additional Resources
- Page ID
- 16157
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Review and assess your learning. Start with the "Important Terms and Concepts" to ensure you know the terminology related to the topic of the chapter and concepts discussed. Move on to the "Review Questions" to answer critical thinking questions about concepts and processes discussed in the chapter. Finally, test your overall understanding by taking the "Self-assessment quiz".
-
- biogeographical realm
- geographical regions out of which assemblages of plants and animals evolved and dispersed
-
- Palaearctic realm
- stretched across Europe, most of Asia, the Mediterranean, North Africa. It is very similar to the Nearctic in terms of the diversity of biomes including tundra, grassland, deciduous and coniferous forest, chaparral, and desert biomes
-
- Nearctic realm
- includes most of North America and Greenland. The Nearctic realm possesses a great diversity of biomes including the tundra, grassland, deciduous and coniferous forest, chaparral, and desert biomes
-
- Neotropical realm
- found throughout most of central and South America is dominated by tropical forests, savannas, and deserts.
-
- Afrotropical realm
- inhabited by tropical forests, savannas, and deserts and is found in Africa south of the Sahara
-
- Australian realm
- has a desert core, surrounded by tropical forest and savanna. The Australian realm boasts a unique variety of plants and animals as they have evolved in isolation from outside influence
-
- Indomalayan realm
- includes much of southeast Asia and is nearly exclusively tropical forest
-
- Antarctic realm
- exhibits a diverse set of ecosystems from temperate forest and grassland in New Zealand to tundra and ice sheets in Antarctica.
-
- Oceanian realm
- includes tropical islands of the Pacific ocean and dominated by tropical forests
-
- biome
- a large stable terrestrial ecosystem
-
- Forest biome
- consists of close growing trees with leaf canopies that generally overlap
-
- Tropical rain forest
- contains trees standing 30 to 55 meters in height, creating a continuous canopy of foliage. The enclosed canopy shades the forest floor, creating an open forest formation
-
- Tropical Monsoon/Seasonal Forest and Scrub
- contains trees of smaller stature than those found in the rain forest; open canopy that creats a dense, closed forest at the floor, or what we think of as a "tropical jungle".
-
- Mediterranean Sclerophyllus Woodland
- consists of low branching trees with small hard leaves and gnarled thick bark
-
- Midlatitude Broadleaf Deciduous and Mixed Forest
- contains evergreen and/or deciduous trees reaching heights of 15 to 25 meters. The broadleaf forest dominates equatorward, while toward the north, conifers intermingle to create a mixed forest. In most cases the forest is an open forest with little under story growth, though some shade tolerant annual species occupy the ground.
-
- Broadleaf evergreen forest
- mild maritime air masses keep conditions moist enough to suppress any summer drought and provide temperatures warm enough to prevent a threat of frost.
-
- Temperate rain forest (Marine west coast forest)
- known for its lush vegetation occurring along narrow margins of the Pacific Northwest in North America. Composed of a few species of broadleaf and needle leaf trees, huge ferns, and a thick undergrowth.
-
- Northern Coniferous forest
- aka boreal forest; dominated by coniferous trees, with hardy deciduous trees like birch mixed in
-
- Boreal forest
- aka northern coniferous forest; dominated by coniferous trees, with hardy deciduous trees like birch mixed in
-
- Taiga
- a more open form of boreal forest with low growing conifers
-
- Savanna biome
- characterized by an extensive cover of grasses with scattered trees. It is a transitional biome between those dominated by forests and those dominated by grasses
-
- Tropical savanna
- An extensive cover of tall grasses, sometimes reaching a height of 3 meters; Most savanna grass is coarse and grows in tufts with intervening patches of bare ground. Scattered, individual trees or small groves of trees are common.
-
- Thorntree and tropical scrub
- characterized by short, thorny trees and shrubs
-
- Midlatitude savanna (Parkland)
- grasses are broken by patches or ribbons of broadleaf trees
-
- Grassland biome
- dominated by grasses of a variety of species, all having adapted to the summer drought common to their semiarid habitat. The broad expanse of the grasslands is occasionally broken by stands of trees.
-
- Prairie
- found on the humid side of the grassland biome and are often referred to as the tall-grass prairie. A favorable annual moisture balance supports a dense ground cover of tall grasses. Grasses range in height between .6 to 1.2 meters (2 to 4 ft.), with some as tall as 8 feet or more
-
- Steppe grassland
- grasses smaller than a half meter (2 ft); toward the drier portions the ground cover becomes sparse with patches of open ground found between clumps of grass.
-
- Desert biome
- has the lightest cover of plants of any biome. Lack of moisture prevents plants from establishing themselves in this harsh climate. Many unique adaptations to the extreme heat and lack of moisture enable some plants to survive
-
- Dry desert
- Extremely dry regions, some places hardly receiving any measurable precipitation during the year. Plant cover is non-existent over much of the dry desert.
-
- Shrub desert
- supports a more diverse community of plants and animals; more precipitation and cooler temperatures help support a more complete ground cover
-
- oasis
- created where the water table is near the surface. Groundwater can be easily extracted to support vegetation and wildlife.
-
- xerophyte
- Plants adapted to drought
-
- deflation
- when wind dislodges particles and transports them away
-
- desertification
- the expansion of dry lands due to poor agricultural practices (e.g. overgrazing, degradation of soil fertility and structure), improper soil moisture management, salinization and erosion, forest removal, and climate change.
-
- Tundra biome
- found at high elevations in mountainous terrain
-
- Arctic tundra
- Short grasses, flowers, and grass-like sedges, along with covers of mosses and lichens are the dominate forms of vegetation in the tundra. Seasonal frost heave disrupts root systems preventing support for tall vegetation; looks like a treeless plain, interrupted by patterned ground and an occasional tree in selected microenvironments
-
- Alpine tundra
- landscape is dotted with small cushion plants, lichens and mosses. Willows are found where moisture is abundant; Vegetation consists of low growing shrubs, cushion plants, small forbs exploding with colorful flowers and lush meadows of sedges and grasses. These plants cover gentle slopes and rock crevices. Rock surfaces are dotted with a cover of lichens and mosses.
Compare and contrast the canopy and forest floors of the tropical rain forests and the tropical monsoon forests.
- Answer
-
The tropical rain forests are considered an open forest while the tropical monsoon is considered a closed forest. The crowns of tropical rain forest trees intermingle creating a dense canopy that inhibits the penetration of light to the surface. This prevents much dense undergrowth to develop on the forest floor. The tropical monsoon forest has a dense undergrowth as the canopy is more open allowing light to the surface.
Describe how the vegetation and climate change going from the Arctic coast of Canada to the Gulf Coast of the United States along the 90th meridian.
- Answer
-
Arctic Tundra (Tundra Climate) -> Northern Coniferous Forest (Subarctic Climate) -> Midlatitude Broadleaf and Mixed Deciduous Forest (Humid Continental) ->Tall Grass Prairie (Humid Continental) ->Southern Coniferous Forest (Humid Subtropical Climate)
Describe how the vegetation and climate change going from the west coast to the east coast of the United States along the 35N parallel.
- Answer
-
Sclerophyllus Woodland (Dry Summer Subtropical Climate) ->Mountain ( Undifferentiated Mountain Climate)-> Cool Shrub Desert (Midlatitude Desert Climate) Short Grass Prairie (Midlatitude Steppe Climate) -> Tall Grass Prairie (Humid Continental Climate) Midlatitude Deciduous Forest (Humid Continental Climate) -> Southern Coniferous Forest (Humid Subtropical Climate).
What is a savanna and which climate(s) is a savanna usually associated with?
- Answer
-
The savanna biome is characterized by drought tolerant grasses with scattered trees. The tropical savanna is associate with the wet/dry tropical climate.
Compare and contrast the vegetation and climate conditions associated with short and tall grass prairies.
- Answer
-
The short and tall grass prairies reflect the climate the flourish under. Short grass prairie, as its name implies, is comprised of short grasses (e.g., little bluestem grasses, generally less than 2 feet tall and will appear in clumps or patches, especially where the climate (midlatitude steppe) is drier. The tall grass prairie lying on the drier side of the humid continental and moist side of the midlatitude steppe has grasses that stand 2 to 4 feet and sometimes taller. Big bluestem grasses and Black-eyed Susans are common plants.
Permafrost is common to the tundra. What is permafrost and how does it influence the habitability of the tundra for both vegetation and humans?
- Answer
-
Permafrost refers to permanently frozen ground. Actually, the ground has two layers which freeze. A surface layer, called the active layer, thaws during the short "summer" and often subsides. Beneath the active layer is the inactive layer which stays frozen throughout the year. Permafrost creates a barrier to the root development. Larger trees can grow along better drained river valleys where the depth to permafrost is greater. The annual freezing and thawing disrupts root systems inhibiting the growth of very tall vegetation. Permafrost creates an unstable surface for the construction of buildings and other structures.
Explain how the vegetation of the Mediterranean woodland has adapted to the dry summer subtropical climate.
- Answer
-
Thick bark and small, waxy leaves are two adaptations to prevent excessive loss of moisture during the severe summer drought experienced in the dry summer subtropical climate.
How does desertification occur?
- Answer
-
Desertification is the expansion of dry lands due to poor agricultural practices (e.g. overgrazing, degradation of soil fertility and structure), improper soil moisture management, salinization and erosion, forest removal, and climate change.
Describe the characteristics of the temperate rain forest (marine west coast forest) and explain what is responsible for them.
- Answer
-
The temperate rain forest is comprised of lush vegetation and home to some of the largest trees on earth, the coast redwoods. It lacks the diversity of species that the tropical rain forest has made up mostly of a few species of broadleaf and needle leaf trees, huge ferns, and thick undergrowth. The lush vegetation is due to its location on the windward slopes of the Cascade and Coast ranges in North America that receive over 100 inches of rainfall.
Describe the characteristics of the Northern Coniferous Forest (boreal forest) and explain how it has adapted to the subarctic climate in which it is found.
- Answer
-
The Northern Coniferous forest is dominated by coniferous trees, with hardy deciduous trees mixed in. Trees in the northern coniferous forest primarily possess pine needles instead of broad leaves like those of the temperate forests to the south. Being dark in color they absorb what little light falls on their surfaces. Retaining their needles at the end of each growing season gives the tree a head start at growth during the spring as they do not have to waste their energy in producing new foliage. The sloping sides of the conical canopy helps catch the low angle sun rays typical of high latitude locations.
- Lianas and epiphytes are typically found in
- the tall grass prairie.
- the southern coniferous forest
- taiga.
- tropical rain forest.
- Chaparral vegetation is closely associated with the
- humid continental climate.
- midlatitude steppe climate.
- dry summer subtropical (Mediterranean) climate .
- northern coniferous forest.
- Taiga is found on the poleward limits of the
- Midlatitude Steppe
- Broadleaf Evergreen forest
- Midlatitude Broadleaf Deciduous Forest
- Northern Coniferous Forest
- Which of the following biogeographical realms is dominated nearly exclusively by tropical forest?
- Neotropical
- Nearctic
- Afrotropical
- Indomalayan
Use this map to answer the following questions.
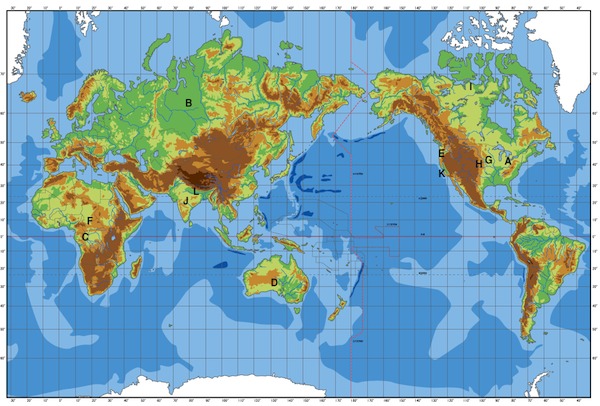
- The most likely location to find a tall grass prairie is
- A
- G
- J
- D
- Xerophytic vegetation is most likely found at
- B
- C
- D
- none of the above
- A temperate rain forest is most likely found at
- C
- F
- H
- E
- A mediterranean woodland is most likely located at
- F
- K
- J
- H
- Which of the following would I most likely find at location H
- Midlatitude Steppe
- Southern Coniferous Forest
- Midlatitude Broadleaf Deciduous Forest
- Northern Coniferous Forest
- Which of the following would I most likely find at location I
- Midlatitude Steppe
- Midlatitude broadleaf deciduous and mixed forest
- Tundra
- Northern Coniferous Forest
- Answer
-
- D
- C
- D
- D
- B
- C
- D
- B
- A
- C
Additional Resources
Use these resources to further explore the world of geography
Connections: "Monitoring Monarchs" NPR (2013) Talk of the Nation report on how habitat loss in Mexico and Miklweed decline in US spells diaster for Monarch butterflies.
World of Change: Amazon Deforestation
Multimedia
"Hot Times in Alaska" Scientific American Frontiers. This episode investigates the impact of climate change on Alaska's ecosystems.
World's Biggest Tiger Preserve - NPR/National Geographic Radio Expeditions visits The Hukawng Valley in Myanmar where an entire valley nearly the size of Vermont is being set aside as a tiger reserve.
"The Birds of the Boreal" NPR/National Geographic Radio Expeditions
"The Last American rain forest" - Morning Edition (NPR) segment from Oct. 22, 1998 reports on the last great temperate rain forest in America, Alaska's Tsongass National Forest. (8:36) (RealAudio Required)
Readings
![]() Grassland Initiative (NASA EOS)
Grassland Initiative (NASA EOS)
Web Sites
![]() Wild World: Terrestrial Ecoregions (NGS/WWF) - rich resource for information about global ecosystems. Organized by biogeographical realm.
Wild World: Terrestrial Ecoregions (NGS/WWF) - rich resource for information about global ecosystems. Organized by biogeographical realm.


