14.4: Geology of Georgia
- Page ID
- 5713
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Overview
Georgia is a wonderful natural laboratory for the study of geology. The rocks within this state span over a billion years of history and through this lens we can study all of the topics presented within this lab manual. Within the state, we have mountains, coastlines, folds, faults, earthquakes, fossils, a diversity of rocks, and evidence of ancient volcanic eruptions. As would be expected with this geologic diversity, Georgia contains multiple physiographic provinces (Figure 14.13) that have been discussed above.
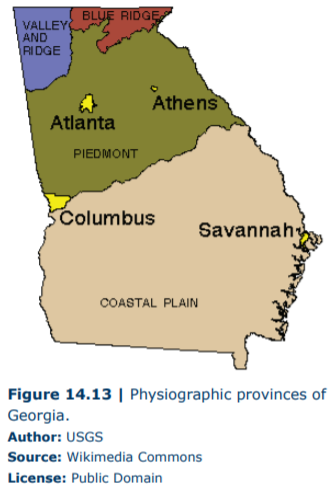
The northwestern portion of the state is within the Valley and Ridge Province and shows the characteristic sandstone ridges with folded and deformed shale within valleys. As you might expect, the shale is relatively soft (which is why they show more deformation) and erodes quickly underneath the massive sandstones. This causes the sandstones to break and tumble downhill making the Rock Cities that are a tourist attraction surrounding Lookout Mountain. The sands are Pennsylvanian in age and interbedded within them are thick coal deposits of ancient forests. These deposits were mined in the past but, for the most part, are not currently active. The northeastern corner of the state is in the Blue Ridge physiographic province, which contains mountains consisting of ancient igneous and metamorphic rock. This area of Georgia contains large protected areas that preserve its natural beauty (such as Chattahoochee National Forest) and contains spectacular waterfalls as seen at Tallulah Falls State Park (Figure 14.14).

The central portion of the state is within the Piedmont Province that consists of rolling hills of igneous and metamorphic rocks punctuated with large batholiths. This region has several important geologic resources. First, the granite within Piedmont has been mined for buildings, monuments, and memorial stones. The granite mining industry is one of the leading producers of granite within the United State, which is centered in Elberton, Georgia. The Piedmont Province has also produced gold, which can be found associated with quartz veins within saprolite (a soft and porous rock often formed by the weathering of granite). Starting around 1830, the discovery of gold in Dahlonega and Villa Rica, Georgia, led to the first major, though short-lived, gold rush.
The largest physiographic province within Georgia is the Coastal Plain in the southern half of the state. The transition from Piedmont into the Coastal Plain is striking in that the topography dramatically changes from rolling hills to flat terrain. The boundary of the Coastal Plain is referred to as the Fall Line, which is a line of waterfalls along the boundary between the provinces caused by differences in the rate of erosion in the two provinces. The rocks and sediments in the Coastal Plain vary from Mid-Mesozoic in the central portion of the state to Late Cenozoic in the southern portion, tracking a fall in sea level through time. The Coastal Plain province has several useful geological resources. Foremost, its organic-rich soil and flat topography make this region ideal for agriculture thus allowing for the abundant production of Georgia’s staples such as peanuts, pecans, onions, cotton, and peaches. The mineral Kaolin, which is a product of the chemical weathering of feldspar, is also mined in this physiographic province. This white clay mineral is used in the production of many products including ceramics, toothpaste, cosmetics, and glossy paper—just to name a few.
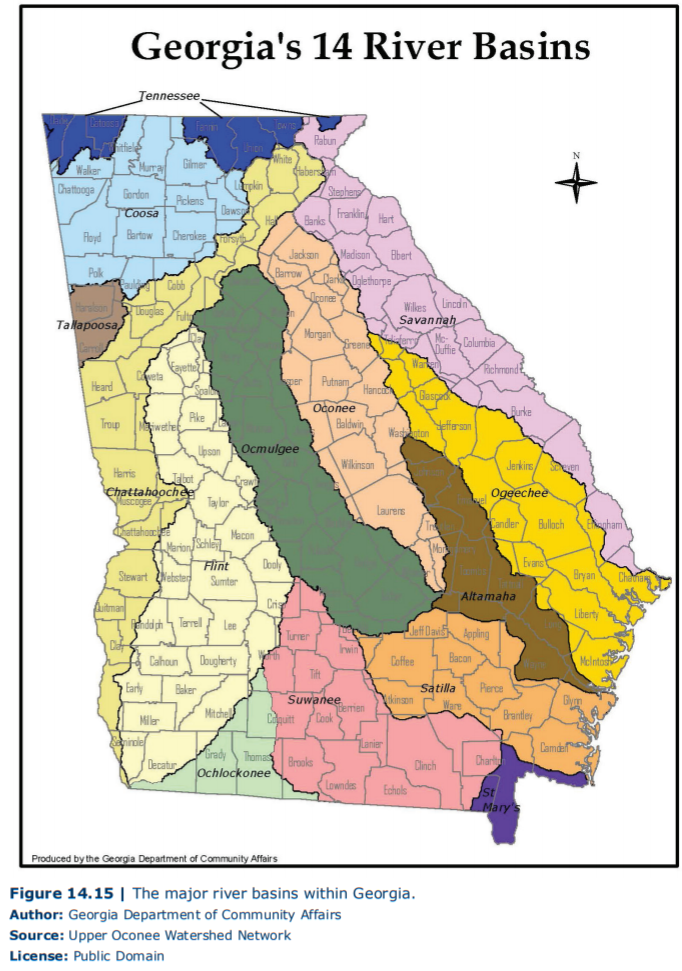
However, one of the most important resources across Georgia is water. As with many parts of the country, Georgia has experienced steady population growth as well as droughts that have made discussions about water reservoirs and usage particularly vital to the future of the state. Georgia contains multiple river basins (Figure 14.15), many of which have been dammed to build large reservoirs, such as Lake Lanier. Study Figure 14.15, and identify the river basins that contain Georgia’s major cities (such as Atlanta, Macon, and Savannah) as well as the river basin in which you live.