3.3: Expanding Universe
- Page ID
- 12774
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\) What did the ancient Greeks recognize as the universe? In their model, the universe contained Earth at the center, the Sun, the Moon, five planets, and a sphere to which all the stars were attached. This idea held for many centuries until Galileo’s telescope helped allow people to realize that Earth is not the center of the universe. They also found out that there are many more stars than were visible to the naked eye. All of those stars were in the Milky Way Galaxy.In the early 20th century, an astronomer named Edwin Hubble discovered that what scientists called the Andromeda Nebula was actually over 2 million light years away, many times farther than the farthest distances that had ever been measured. Hubble realized that many of the objects that astronomers called nebulas were not actually clouds of gas, but were collections of millions or billions of stars that we now call galaxies.
What did the ancient Greeks recognize as the universe? In their model, the universe contained Earth at the center, the Sun, the Moon, five planets, and a sphere to which all the stars were attached. This idea held for many centuries until Galileo’s telescope helped allow people to realize that Earth is not the center of the universe. They also found out that there are many more stars than were visible to the naked eye. All of those stars were in the Milky Way Galaxy.In the early 20th century, an astronomer named Edwin Hubble discovered that what scientists called the Andromeda Nebula was actually over 2 million light years away, many times farther than the farthest distances that had ever been measured. Hubble realized that many of the objects that astronomers called nebulas were not actually clouds of gas, but were collections of millions or billions of stars that we now call galaxies.
Hubble showed that the universe was much larger than our own galaxy. Today, we know that the universe contains about a hundred billion galaxies, about the same number of galaxies as there are stars in the Milky Way Galaxy. After discovering that there are galaxies beyond the Milky Way, Edwin Hubble went on to measure the distance to hundreds of other galaxies. His data would eventually show how the universe is changing, and would even yield clues as to how the universe formed. Today we know know that the universe in nearly 14 billion years old.
Redshift
If you look at a star through a prism, you will see a spectrum, or a range of colors through the rainbow. The spectrum will have specific dark bands where elements in the star absorb light of certain energies. By examining the arrangement of these dark absorption lines, astronomers can determine the composition of elements that make up a distant star. In fact, the element helium was first discovered in our Sun, not on Earth, by analyzing the absorption lines in the spectrum of the Sun.
While studying the spectrum of light from distant galaxies, astronomers noticed something strange. The dark lines in the spectrum were in the patterns they expected, but they were shifted toward the red end of the spectrum, as shown in Figure below. This shift of absorption bands toward the red end of the spectrum is known as redshift.
Redshift occurs when the light source is moving away from the observer or when the space between the observer and the source is stretched. What does it mean that stars and galaxies are redshifted? When astronomers see redshift in the light from a galaxy, they know that the galaxy is moving away from Earth. What astronomers are noticing is that all the galaxies have a redshift, strongly indicating that all galaxies are moving away from each other causing the Universe to expand.
Redshift can occur with other types of waves too, called the Doppler Effect. An analogy to redshift is the noise a siren makes as it passes you. You may have noticed that an ambulance seems to lower the pitch of its siren after it passes you. The sound waves shift towards a lower pitch when the ambulance speeds away from you. Though redshift involves light instead of sound, a similar principle operates in both situations. Check out this animation of the Doppler Effect.

The Expanding Universe
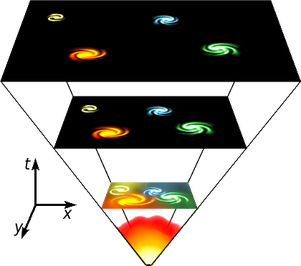 Edwin Hubble combined his measurements of the distances to galaxies with other astronomers’ measurements of redshift. From this data, he noticed a relationship, which is now called Hubble’s Law. The law states that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from us. What this leads to is the hypothesis that the universe is expanding. Check out this animation demonstrating the expanding universe. The figure here by NASA shows a simplified diagram of the expansion of the universe. If you look closely at the diagram, you that on the left was the formation of the universe and the energy is quite high. Over the course of the 13.7 billion years, the energy begins to cool enough to create trillions of stars and over time develop into galaxies. Over time, the galaxies continue to cool and expand farther apart from each other.
Edwin Hubble combined his measurements of the distances to galaxies with other astronomers’ measurements of redshift. From this data, he noticed a relationship, which is now called Hubble’s Law. The law states that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from us. What this leads to is the hypothesis that the universe is expanding. Check out this animation demonstrating the expanding universe. The figure here by NASA shows a simplified diagram of the expansion of the universe. If you look closely at the diagram, you that on the left was the formation of the universe and the energy is quite high. Over the course of the 13.7 billion years, the energy begins to cool enough to create trillions of stars and over time develop into galaxies. Over time, the galaxies continue to cool and expand farther apart from each other.
- Dynamic Earth: Introduction to Physical Geography. Authored by: R. Adam Dastrup. Located at: http://www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html. Project: Open Geography Education. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Andromeda galaxy. Authored by: JPL-Caltech. Provided by: NASA. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Andromeda_galaxy_2.jpg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Schema Redshift. Authored by: Rogilbert. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Schema_Redshift.png. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Universe expansion. Authored by: Gnixon. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Universe_expansion2.png. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright

