16.7: Adaptations to the Marine Environment
- Page ID
- 10422
Adaptations to the Marine Environment
• Ability to float (Zooplankton – some produce fats or oils to stay afloat)
• Ability to swim (Nekton – larger fish and marine mammals)
Propulsion and movement of fish - the body plan of fish reflect adaptations to feeding on prey and fleeing predators.
Width/Length Ratio
Tuna - .28
Dolphin - .25
Swordfish - .24
Whale - .21
Most efficient is about.25, but there is a size-scale factor.
Ratio produced from natural selection “the fittest survive and produce offspring”

Compare with Surfboard Design!
| Type | Width | Length | Ratio | Comments |
| Short Board | 19 ¼" | 6’4” | 0.25 | Small – medium waves |
| PT (Ebenizer Townsend, 1798) | 19 ¼" | 6'7" | 0.24 | Large waves |
| Average Long Board | 22" | 9'0" | 0.20 | Like a whale – scale factor |
| Average Surf Board | 18 ¼" | 6’2” | 0.25 | rapid turns, harder to control |
Kinds of Zooplankton
Includes organisms described as floaters and drifters. All forms are invertebrates.
Microscopic Zooplankton include:
Radiolarians, Foraminifers, Copepods
Macroscopic Zooplankton:
• Krill ( resemble mini shrimp or large copepods, critical in Antarctic food chains)
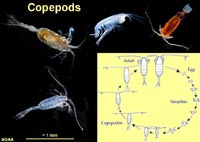 |
 |
| Figure 16.43. Copepods | Figure 16.44. Krill |
Floating Macroscopic Zooplankton include:
• Portuguese man-of-war (have gas-filled float)
• Jellyfish (have soft, low-density bodies; there are hundreds of species)
Many species of portuguese man-of-war and jellyfish can sting or produce potent toxins.
 |
 |
| Figure 16.45. Portuguese man-of-war | Figure 16.46. Jellyfish |
Swimming (Nekton) Organisms
Includes all fish, squids, sea turtles and sea snakes, and marine mammals.
• Swim by trapping water and expelling it (squid, octopus)
• Swim by curving body from front to back (fish, etc.)

Adaptations for Finding Prey
• Lungers wait for prey and pounce (grouper).
• Cruisers actively seek prey (tuna).
 |
 |
| Figure 16.48. Groupers are lungers | Figure 16.49. Tuna are cruisers |
Adaptations to Avoid Predation
• Speed
• Hiding: includes Transparency, Camouflage and Countershading
• Poison (to touch or eat: examples: sea snakes, blowfish, lion fish)
• Schooling (safety in numbers, appear as a larger unit, maneuvers confuse predators)

| Video: Schooling anchovies at Scripps Pier (Scripps Institute of Oceanography) |


