2.16: Permian Period (299 to 252 million years)
- Page ID
- 9784
Permian Period (299 to 252 million years)
The last period of the Paleozoic Era was a time of colossal changes. All the continents of the world had combined to form the supercontinent of Pangaea. In the fossil record, a group of tetrapods (lizard-like, four legged animals with backbones or spinal columns) called amniotes appeared, capable of living on dry land and producing terrestrially adapted eggs. All modern land species are descendant from a common ancestral group of amniotes. Reptiles adapted and flourished in the more arid conditions.
During the Permian, the expansive fern forests that existed during the Carboniferous disappeared, and vast desert regions spread over the North American continental interior. Seed-bearing conifers (gymnosperms) first appear in the Permian fossil record.
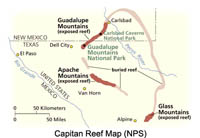
In Permian time, seawater began to flood the great rift valleys associated with the opening of the Atlantic Ocean basin and the separation of North America and South America. One arm of the sea flooded westward into an inland sea basin located in the West Texas and New Mexico region (Figure 2.35). Great reef tracks developed in around this basin Figure 2-36). Eventually the Permian Basin (as it is called) completely filled in with massive accumulations of salts (gypsum and evaporite).
The end of the Permian Period (and Paleozoic Era) is marked by the greatest mass extinction in Earth history.