5.1: Looking at the Whole Cloud
- Page ID
- 5105
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
Putting It All Together
We can put all of the processes from this lesson together to look at the lifecycle of a cloud:
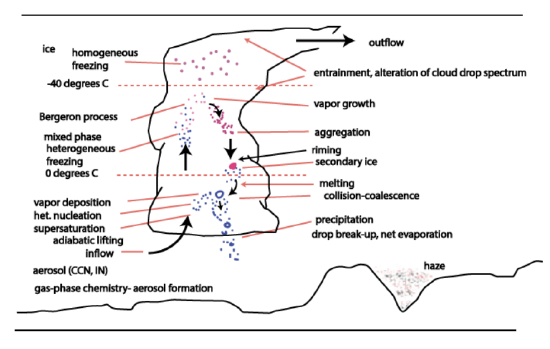
The following is a description of convection’s stages of development:
- Local perturbation in atmospheric density fields, sometimes driven by uneven surface heating or moisture evaporation, starts relative vertical motion
- Stage 1: “Developing Stage” (also called Cumulus Stage)
- Updraft dominates center of cloud, cloud drops form and grow
- Release of latent heat provides the energy for vertical motion and growth
- Stage 2: “Mature Stage”
- Downdrafts form in addition to updrafts, causing gust fronts
- Cloud reaches height so that freezing occurs and precipitation develops
- Evaporation of precipitation drives downdrafts
- Stage 3: “Dissipating Stage”
- Downdrafts only
- Water mass is removed by sedimentation/evaporation
The video below (2 min.) includes some great time-lapse video of clouds forming and disappearing. Check it out:
Quiz 5-4: How precipitation forms.
- You can take Practice Quiz 5-4 as many times as you like.
- When you feel you are ready, take Quiz 5-4. You will be allowed to take this quiz only once. Good luck!

