1.8: Activity 1G - Measuring Angles
- Page ID
- 14602
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
You will need the following equipment for these lab activities:
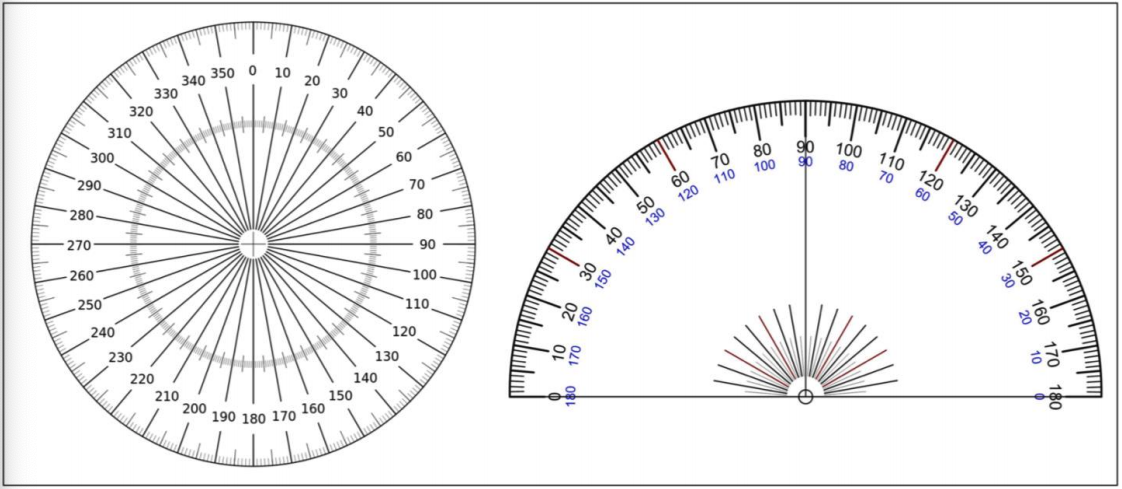
- Protractor; tutorial on how to use a protractor.
- 360 Protractor (Note: both protractors can be printed. Print on transparency for best results.)
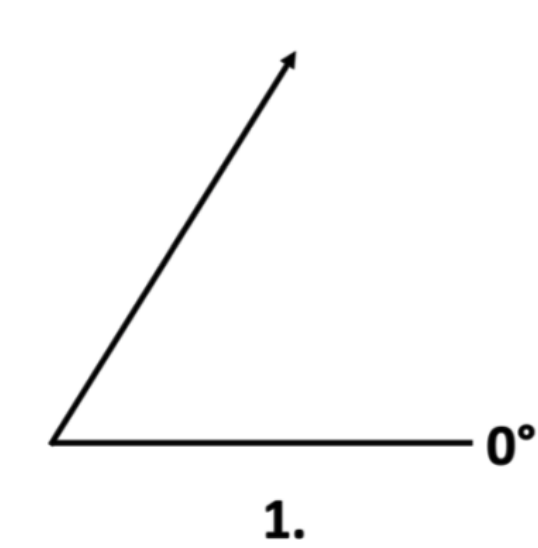
1. Using your protractor, measure the angle of the arrow below.
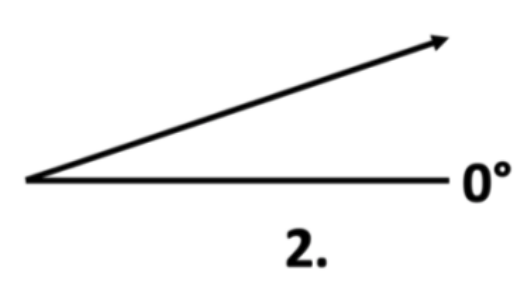
2. Using your protractor, measure the angle of the arrow below.
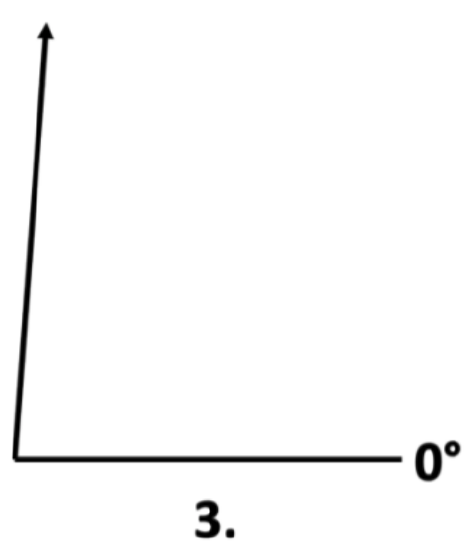
3. Using your protractor, measure the angle of the arrow below.
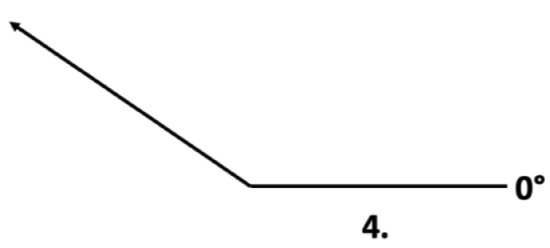
4. Using your protractor, measure the angle of the arrow below.
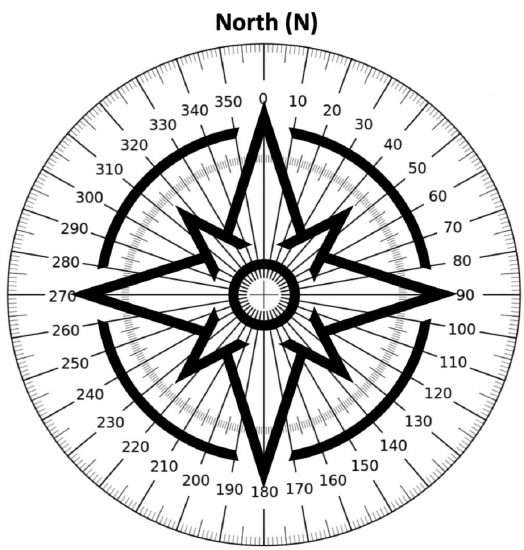
5. Below is a compass rose, which indicates the cardinal directions. North (N) is always represented as 0°/360°. On the compass below, label:
a. The remaining cardinal directions (S, W, E) in black.
b. The intermediate points (NE, SE, NW, SW) in brown.
c. The intermediate points of the intermediate points (NNE, ENE, ESE, SSE, SSW, WSW, NNW, WNW) in blue.
Attributions
- Figure 1.12: Derivative of Left: “Protractor Rapporteur Degree V1” (CC-BY-SA 3.0; Autiwa via Wikimedia Commons ) and Right: “Rapporteur” (Public Domain; Scientif38 via Wikimedia Commons) by Chloe Branciforte
- Figure 1.13: “Angles for measurement” (CC-BY 4.0; Chloe Branciforte, own work)
- Figure 1.14: Derivative of “Protractor Rapporteur Degree V1” (CC-BY-SA 3.0; Autiwa via Wikimedia Commons) by Chloe Branciforte


